Imagine this: you sell 1,000 products in March but wait until April to account for the production costs. As a result, your finances show huge profits in March and a surprising dip in April – and here’s how you come to a confusion.
That’s the essence of the expense recognition principle – making sure expenses are logged in the same period as the revenues they contribute to.
Read: A Complete Guide to Financial Statement Analysis for Strategy Makers
For CFOs, this principle is actually a strategic tool. Proper expense recognition impacts profit margins, cash flow, and decision-making.
Why, how, and what to expect in practice – let’s find out.
What is the Expense Recognition Principle
With the expense recognition principle is all about timing – it makes sure expenses are recorded in the same period as the revenues they help bring in. Think of it as a financial duet: revenue and its related expenses need to perform together in perfect harmony. It’s a key part of accrual accounting, which focuses on when financial events happen, not just when payments are made or received.
Let’s go back to the example from the beginning – so you’ve sold 1000 products in March, right? Well, the cost of producing those products – materials, labor, everything – should also be recorded in March, even if you don’t pay your suppliers until April. Why? Because those expenses are part of the story behind your March sales.
The expense recognition principle makes your financial statements accurate and meaningful. No wild swings in profit one month and losses the next – just a clear, consistent picture of how your business is really doing.
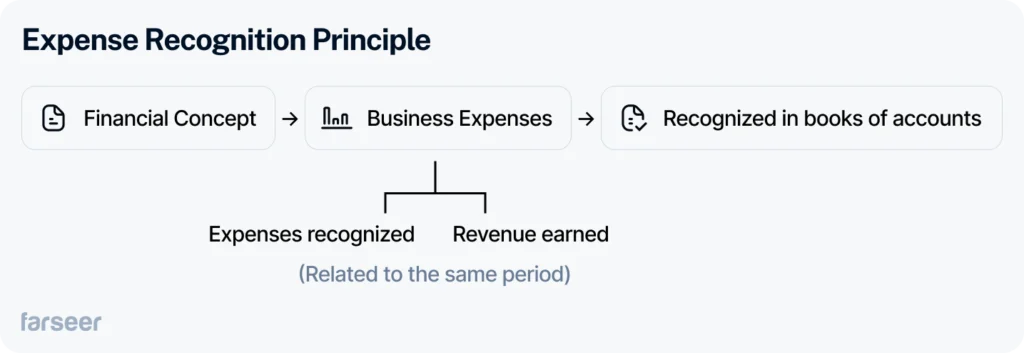
How the expense recognition principle aligns with accrual accounting
Let’s go one step back. The expense recognition principle depends mainly on the accounting method your business is using. There are two – accrual and cash accounting. What’s the difference?
Cash accounting records expenses only when money is transferred. On the other hand, accrual accounting matches expenses to the revenue they help generate.
Think of a manufacturing company producing car parts. They might buy raw materials in January, but sell the finished parts in February. With accrual accounting, the cost of those materials gets recorded in February, with the sales revenue, giving a clearer picture of how profitable the business really is. If they were using cash accounting, the expenses would show up in January and the revenue in February. In this way, it’s harder to see the connection between costs and earnings.
Feels like the definition of accrual accounting matches the one of the expense recognition principle? Agreed – but here’s the difference. Accrual accounting is the comprehensive framework, while the expense recognition principle is one of the key principles that guide how expenses are handled within that framework.

How Does the Expense Recognition Principle Work in Practice
Maybe the best way to demonstrate how the principle works is through an example. Let’s say we have an energy company dealing with long-term contracts. There are 2 steps:
Step 1: Match expenses to revenue
Imagine an energy company that signs a two-year contract to supply electricity to a corporate campus for a fixed monthly fee. At the start of the deal, the company installs some specialized equipment, which comes with a big cost. With the expense recognition principle involved, you won’t record the entire cost of the equipment right away. Instead, you’ll spread it evenly over the two years, matching it with the monthly revenue from the fixed fees. In this way, the company’s books will show a more accurate picture of how the costs and revenue are connected throughout the contract.
Step 2: Implement it in reporting
Every month the finance team updates the books by recording part of the equipment cost as an expense. Let’s say the equipment costs $24,000, and the contract lasts 24 months – they’d show $1,000 each month as the expense. This will keep the profitability numbers accurate and in line with the revenue earned.
This is important for 2 reasons – primarily, it follows accounting rules, but it also gives stakeholders a clear view of how the company is performing financially over time.

Common Challenges and Mistakes
Though it sounds pretty simple, all of this comes with a range of challenges.
Here are some of them:
- Timing issues. Recording expenses when cash is paid instead of incurred. Also, costs that are related to long-term contracts or projects are sometimes recorded all at once rather than spread out to match the revenue.
- Wrong classification of expenses. It can happen that you classify regular expenses as capital investments or vice versa – that can distort financial reports heavily. Additionally, mistakes happen if you assign expenses to wrong departments or projects.
- Challenges in global operations or multinational company accounting. Companies that operate in different regions may have problems aligning these recognition practices because of different local accounting rules or currencies.
- Human errors (manual processes). If all of this is done manually, there is a huge risk of calculation mistakes, missed entries and other inconsistencies.
How to avoid these mistakes
There are several things you can do to avoid these mistakes.
For starters, it’s important to create and enforce clear policies on when and how expenses should be recognized across the whole organization or company.
Next – regular training for the finance team will help keep everyone up-to-date on the latest standards and best practices. Also, investing in modern tools like Farseer can streamline the whole process, minimize manual errors, and ensure compliance with accounting standards. And last but not least – conducting regular reviews and audits is crucial if you’re keen on digging out errors and ensuring that policies are being applied as they should be.
Role of FP&A Software in Expense Recognition
FP&A software, such as Farseer, revolutionizes the way businesses manage expense recognition by automating and streamlining the process. These tools are designed to minimize human error, ensure compliance with accounting standards, and provide CFOs with real-time financial insights for better decision-making.
Key features that help expense recognition
- Automation: The tool automatically matches expenses with revenues, so you don’t have to worry about doing it manually. This keeps everything in line with the expense recognition principle, reduces errors, and saves your financial team a ton of time.
- Real-time tracking: It keeps an eye on expenses and revenues as they happen, so you get up-to-the-minute insights. This means the world for your forecasting accuracy and takes your financial planning to the next level.
- Compliance support: The software makes it easier to align with accounting standards such as GAAP or IFRS. This reduces the risk of regulatory penalties and makes you ready for an audit at any point.
Conclusion
Getting the expense recognition principle right is key to keeping your finances on track and earning the trust of your stakeholders. When you match expenses with the revenue they help generate, CFOs can stay compliant, make smarter decisions, and set up a solid foundation for growth.
FP&A tools like Farseer make this all a lot easier with automation, real-time tracking, and built-in compliance features, so your finance team can focus on what really matters. Want to make expense recognition a breeze? Give Farseer a try and see how it can help you streamline your process!